Definition
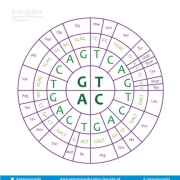
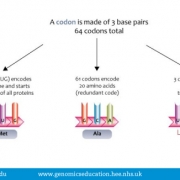
A sequence of three bases within DNA or RNA that encode for a particular amino acid – that is, they contain the instructions for the placement of a particular amino acid when producing a polypeptide.
Use in clinical context
Changes to the bases within a codon can have a variety of effects on the resulting amino acid and polypeptide. Often there is no effect at all as most amino acids are coded for by multiple codons. For example, GGT and GGC both code for the amino acid Glycine, therefore the DNA change will not affect the amino acid or the polypeptide. Other changes to the codon can affect the resulting amino acid, for example GGT changed to GAT changes the amino acid Glycine to an Aspartic acid. This may or may not result in significant changes to the polypeptide, but it is possible that this small change can have a large functional effect. Other changes can insert or delete bases that can affect several codons at once, significantly impacting the final protein.
Related terms
Amino acids | Bases | Protein