Use in clinical context
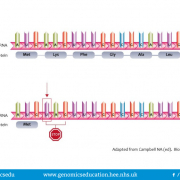
Sometimes a change in the DNA sequence of a gene results in the creation of an early stop codon. The function of a stop codon is to end translation, therefore if a premature stop codon is introduced then a shortened or truncated protein may be produced. This type of variant can have serious functional consequences. For example, truncating variants in the SCN1A gene lead to Dravet syndrome which, although rare, can lead to severe epilepsy which can result in developmental disability.
Related terms
Codon | Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) | Gene | Genetic/genomic variation | Protein | Sequence | Translation