Use in clinical context
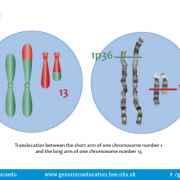
There are a range of possible types of genomic variant, some of which alter the structure of the genome. Sections of the genome can be added (insertions), removed (deletions), rearranged (translocations) and duplicated (duplications). The size of the variant does not correspond to the size of the effect. Large portions of chromosomes can be moved from one to the other with no apparent ill effects. Conversely, single base deletions or additions within a gene can put the whole of the reading frame out resulting in a nonsense mRNA and resulting protein. Karyotyping, FISH and microarrays can be used to look for structural variants depending on the size.
Related terms
Bases | Chromosome | Deletions | Gene | Messenger RNA | Protein | Translocation