Definition
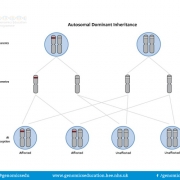
Autosomal dominant conditions are caused by variants in genes on one of the 22 autosomal chromosomes. The condition presents in the heterozygous state, where the pathogenic variant is present in only one copy of the gene.
Use in clinical context
Humans usually have two copies of each autosome, and therefore two copies of each gene. With autosomal dominant conditions, symptoms associated with the condition present when one copy of the gene has the pathogenic variant, while the other copy is unaltered. However, additional factors can influence the development of these conditions; in some cases, signs and symptoms of the condition may not present, even in the presence of the pathogenic variant.
Related terms
Autosomes | Gene | Gene expression | Genetic/genomic variation | Penetrance | Phenotype | Recessive allele | Recessive phenotype