Copy number variants
A copy number variant is a type of structural genomic variant that arises as a result of a duplication or deletion of a region of DNA.
How do copy number variants arise?
Although the mechanism is not fully understood, one theory that could explain copy number variants (CNVs) is that during the complicated process of replication, chromosome sections can be either lost or duplicated due to unequal crossing over between homologous repetitive regions of DNA. This phenomenon is known as non-allelic homologous recombination.
What are CNVs?
CNVs are a type of structural variant. Research suggests that they may account for up to 9.5% of the human genome.
The different types of CNV that can occur are:
- deletions and microdeletions: when sections of the genome have been deleted, resulting in loss of genetic material; and
- duplications and microduplications: when sections of the genome have been duplicated, resulting in a gain of genetic material.
See figure 1 for some examples of CNVs in action.
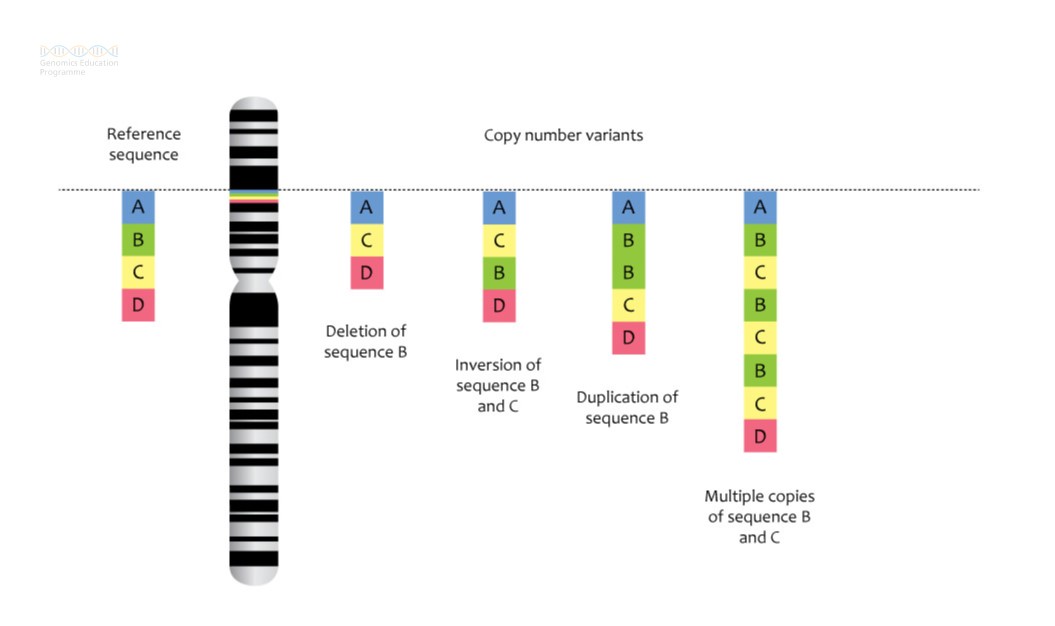
Figure 1: Deletions and microdeletions result in loss of genetic material, while duplications and microduplications result in gain of genetic material.
Use in clinical context
CNVs often result in too much or too little protein being produced, which can in turn influence gene expression and/or contribute to disease.
Tumour cells often have structural variants that result in CNVs.
One of the most well-known examples of a disease that is caused by a CNV is Huntingdon’s disease, which is caused by a repeating sequence of three base pairs (known as a trinucleotide repeat) at the end of the coding region of the HTT gene; people with 40 or more repeats are affected by Huntington’s disease.
CNVs at many recurrent genome hotspots are also associated with epilepsy.
Key messages
- CNVs are regions of our genome that vary in the number of copies present, due to either duplication or deletion.
- CNVs are classed as structural changes, and they may account for up to 9.5% of the human genome.
- As well as contributing to normal genomic variation, CNVs can also cause disease or influence gene expression.
Resources
For clinicians
- National Genomics Education Programme: What are copy number variants?
References:
- Zarrei M, MacDonald JR, Merico D and others. ‘A copy number variation map of the human genome‘. Nature Reviews Genetics 2015: volume 16, pages 172–183. DOI: 10.1038/nrg3871
For patients
- Unique: Understanding Chromosome and Gene Disorders: Deletions and microdeletions (PDF, two pages)
- Unique: Understanding Chromosome and Gene Disorders: Duplications and microduplications (PDF, two pages)